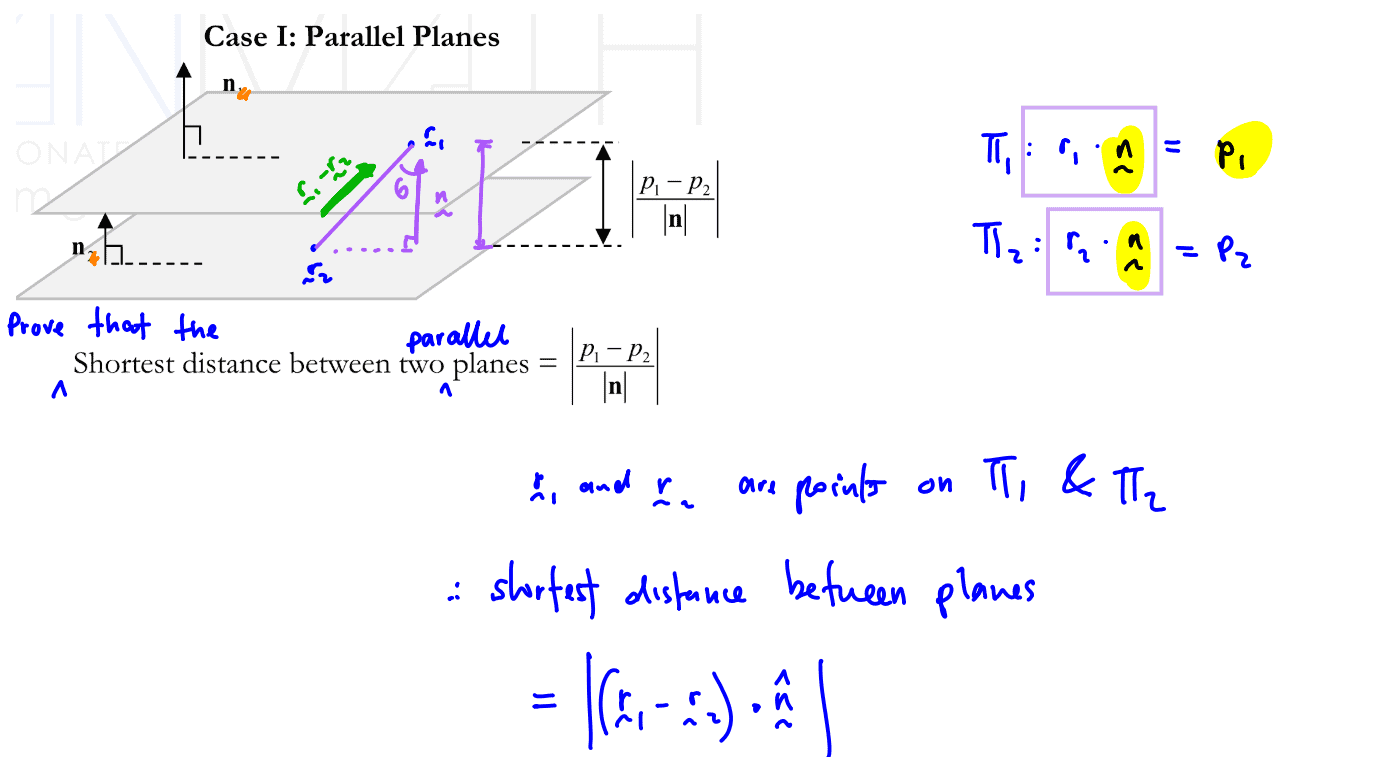
The distance between two parallel lines in the plane is the minimum distance between any two points.
Formula and proof
Because the lines are parallel, the perpendicular distance between them is a constant, so it does not matter which point is chosen to measure the distance. Given the equations of two non-vertical parallel lines
the distance between the two lines is the distance between the two intersection points of these lines with the perpendicular line
This distance can be found by first solving the linear systems
and
to get the coordinates of the intersection points. The solutions to the linear systems are the points
and
The distance between the points is
which reduces to
When the lines are given by
the distance between them can be expressed as
See also
- Distance from a point to a line
References
- Abstand In: Schülerduden – Mathematik II. Bibliographisches Institut & F. A. Brockhaus, 2004, ISBN 3-411-04275-3, pp. 17-19 (German)
- Hardt Krämer, Rolf Höwelmann, Ingo Klemisch: Analytische Geometrie und Lineare Akgebra. Diesterweg, 1988, ISBN 3-425-05301-9, p. 298 (German)
External links
- Florian Modler: Vektorprodukte, Abstandsaufgaben, Lagebeziehungen, Winkelberechnung – Wann welche Formel?, pp. 44-59 (German)
- A. J. Hobson: “JUST THE MATHS” - UNIT NUMBER 8.5 - VECTORS 5 (Vector equations of straight lines), pp. 8-9